Spleen vasculature - Erler Zimmer 3D anatomy Series MP1132
erler zimmerMade in ultra-high resolution 3D printing in full color.
Spleen Vascularization - Erler Zimmer 3D anatomy Series MP1132
This Spleen Vascularization model is part of the exclusive Monash 3D anatomy series, a comprehensive series of human dissections reproduced with ultra-high resolution color 3D printing.
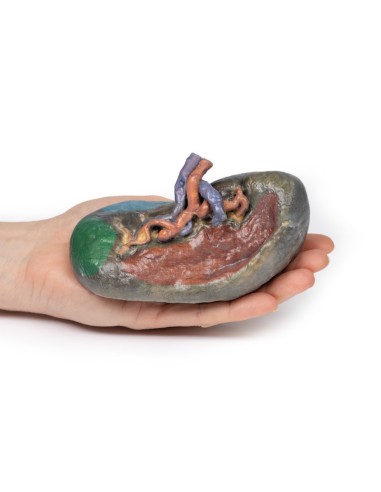
At the splenic hilum, the splenic artery and vein can be seen entering the spleen to supply and drain the organ. The splenic vein opening was kept pervious by inserting silicone tubing into the model. This model shows that the uppermost branch of the splenic vein has been dissected from its normal passage into the spleen. One can appreciate the "tortuous" twisted shape of the splenic artery branching at the hilum. This reflects the overall curled and twisted shape of the vessel through its course from the celiac trunk to the spleen.
The splenic artery and vein give rise to a short gastric vasculature as well as the left gastro-omental vasculature. In this specimen, the splenic artery and vein were cut after these vessels branched, and thus cannot be seen in the model.
The splenorenal ligament connects the spleen to the left kidney and contains the splenic artery, splenic vein, and tail of the pancreas. It is formed by overlapping the peritoneum that was originally part of the dorsal mesentery during embryologic development over this vascular system. The splenorenal ligament is not observable on the model because the peritoneum was removed to expose the splenic vasculature.
The gastrosplenic ligament connects the stomach to the spleen and contains the short gastric arteries and part of the left gastro-omental artery at its origin as it branches from the splenic artery. Like the splenorenal, the gastrosplenic ligament is formed by overlapping the peritoneum that was originally part of the dorsal mesentery during embryologic development. The gastrosplenic ligament is not present because the splenic artery was dissected after its formation.
The exterior of the spleen consists of a thin fibrous capsule. Because of its delicate nature and the large amount of blood usually contained in the spleen, the fibrous capsule is vulnerable to rupture.
What advantages does the Monash University anatomical dissection collection offer over plastic models or plastinated human specimens?
- Each body replica has been carefully created from selected patient X-ray data or human cadaver specimens selected by a highly trained team of anatomists at the Monash University Center for Human Anatomy Education to illustrate a range of clinically important areas of anatomy with a quality and fidelity that cannot be achieved with conventional anatomical models-this is real anatomy, not stylized anatomy.
- Each body replica has been rigorously checked by a team of highly trained anatomists at the Center for Human Anatomy Education, Monash University, to ensure the anatomical accuracy of the final product.
- The body replicas are not real human tissue and therefore not subject to any barriers of transportation, import, or use in educational facilities that do not hold an anatomy license. The Monash 3D Anatomy dissection series avoids these and other ethical issues that are raised when dealing with plastinated human remains.