Chest dissection with heart and vessels - Erler Zimmer 3D anatomy Series MP1122
erler zimmerMade in ultra-high resolution 3D printing in full color.
Chest dissection with heart and vessels - Erler Zimmer 3D anatomy Series MP1122
This model is part of the exclusive Monash 3D anatomy series, a comprehensive series of human dissections reproduced with ultra-high resolution color 3D printing.
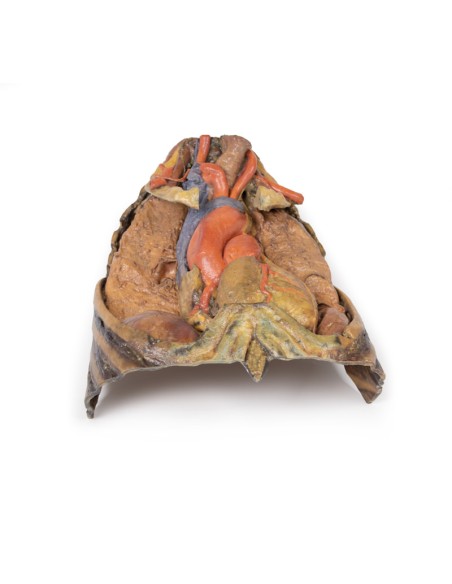
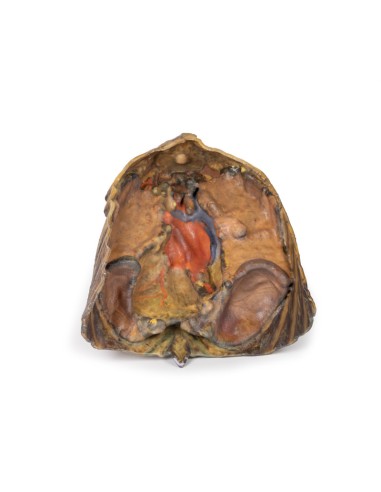
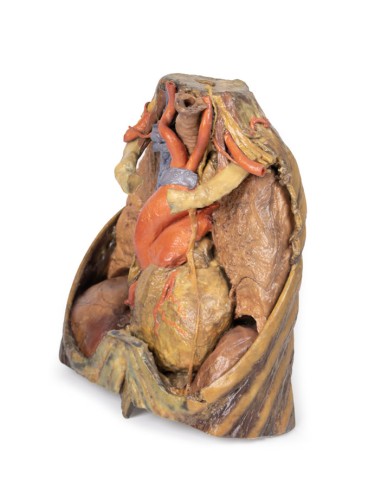
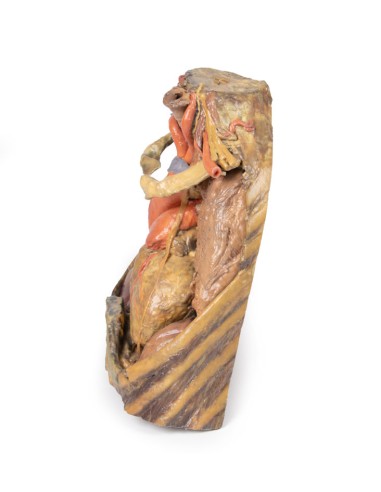
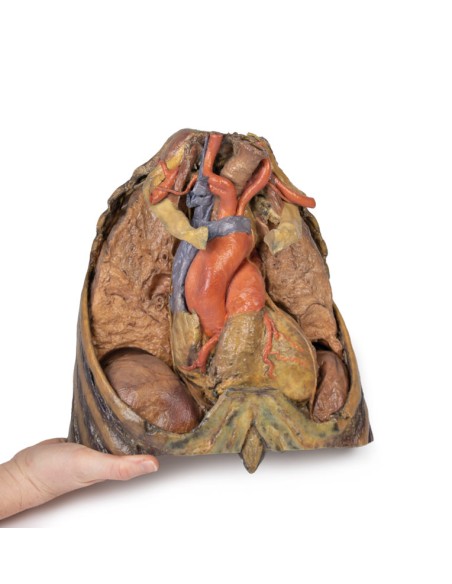
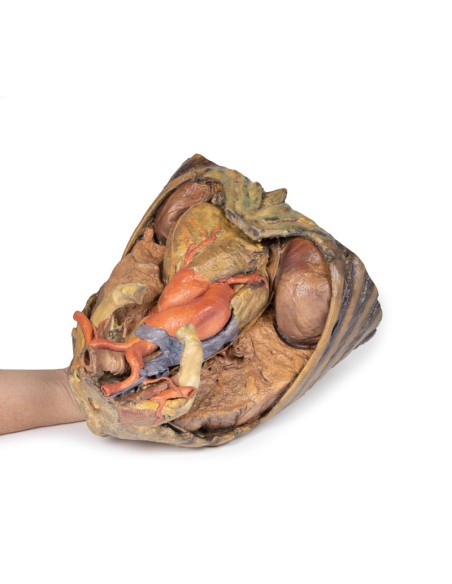
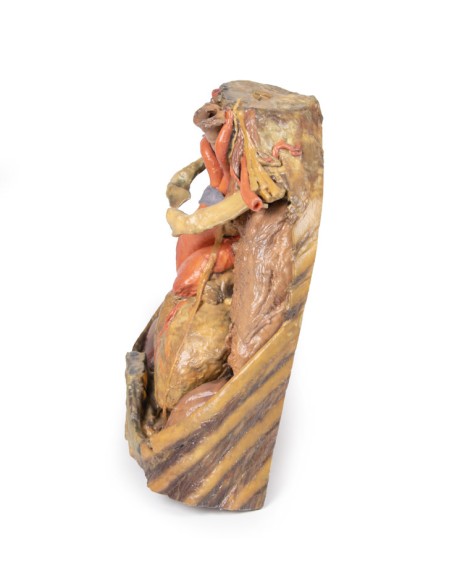
The upper thoracic opening contains structures that emerge from the chest and enter the head, neck, and upper limb. In this specimen, both clavicles, key venous structures, and other musculature were removed. Despite this, other important components of the anatomy can be observed. Key structures include the trachea seen more superiorly with a thick ring of cartilage, a rib was exposed before meeting its costal cartilage, traveling in a lateral to medial direction, and the anterior scalene muscle that inserts into the rib at the top.
In terms of blood supply, the right subclavian can be seen superior to the rib, yielding the thyrocervical trunk to supply the neck, the left subclavian can also be seen superior to the rib, issuing the suprascapular artery, and both the left and right common carotid can be seen superiorly with the left also containing a clear left vagus nerve.
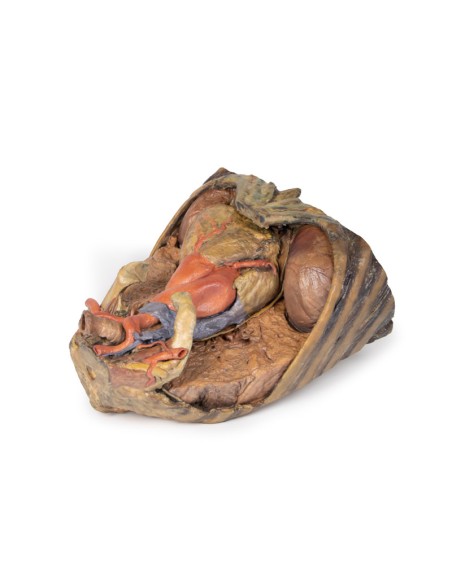
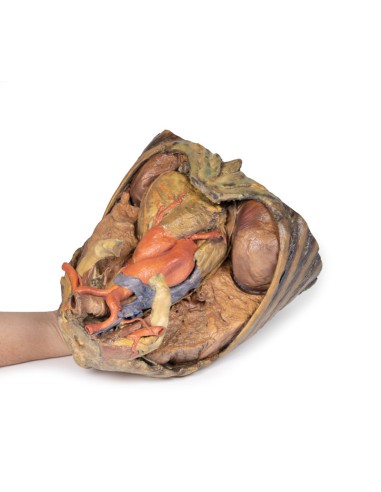
Traveling inferiorly from the skull, the vagus nerve follows the common carotid arteries into the carotid sheath that can be seen in the left common carotid artery. The left phrenic nerve remains unclear until it emerges in the mediastinum. Components of the left brachial plexus are visible, from roots to trunks. Numerous smaller branches recede, including the dorsal scapular nerve.
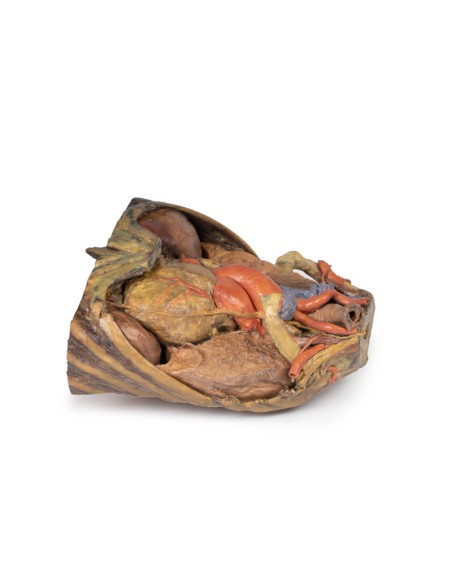
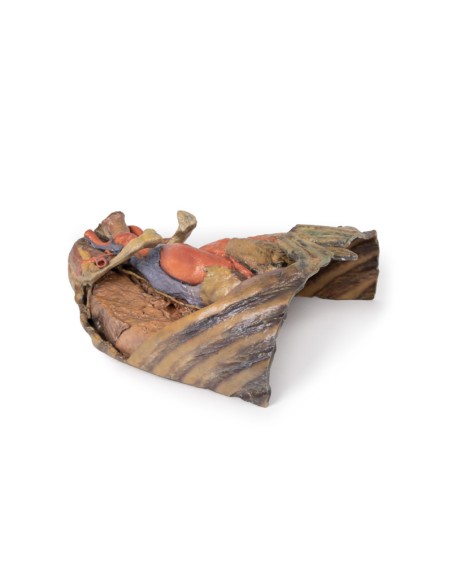
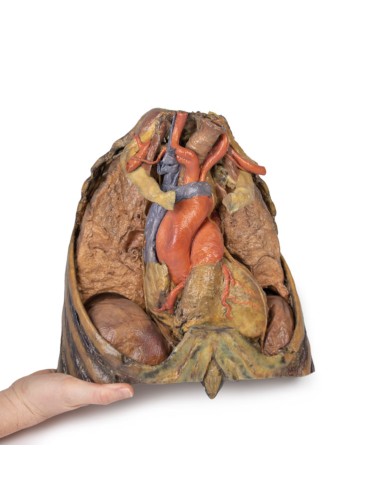
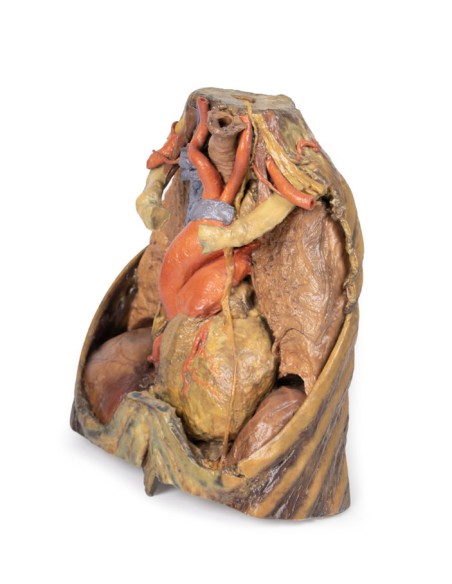
In the mediastinum, key structures can be identified in the thoracic mediastinum. However, other pieces of anatomy including the inferior vena cava, right vagus nerve and some coronary vessels cannot be observed in this specimen. The right phrenic nerve can be traced posterior to the heart; this was moved from its normal anterior position to that of the heart during dissection. You can also see the left phrenic nerve is still contained in its connective tissue and remains located anterior to the heart until it reaches the diaphragm for innervation. The left vagus nerve can be seen posterior to the heart and is easier to identify superiorly by following the left common carotid artery into the carotid sheath. Note the left recurrent laryngeal nerve moving under the aorta.
The arch of the aorta gives brachiocephalic and left common carotid branches superior to the heart. The left subclavian artery can be seen just posterior to the left common carotid artery. With the pulmonary trunk exiting immediately superior to the heart. The left anterior descending carotid artery can be seen cascading anteriorly over the heart with the superior vena cava to the right of the aorta and posterior.
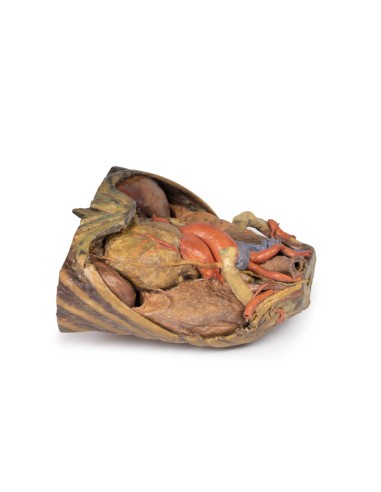
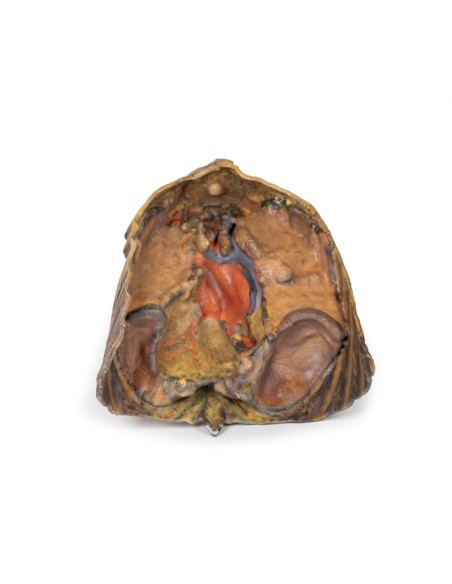
The lower thorax shows ribs 8 to 12 on the specimen, the musculature between these ribs can also be seen. In particular, the direction of the external intercostal muscle inferomedially can be seen as it progresses into a layer of fascia.
As observed in the specimen, the right hemidiaphragm is located more superiorly than the left hemidiaphragm, and this is due to the presence of the liver on the right side of the abdominal cavity.
What advantages does the Monash University anatomical dissection collection offer over plastic models or plastinated human specimens?
- Each body replica has been carefully created from selected patient X-ray data or human cadaver specimens selected by a highly trained team of anatomists at the Monash University Center for Human Anatomy Education to illustrate a range of clinically important areas of anatomy with a quality and fidelity that cannot be achieved with conventional anatomical models-this is real anatomy, not stylized anatomy.
- Each body replica has been rigorously checked by a team of highly trained anatomists at the Center for Human Anatomy Education, Monash University, to ensure the anatomical accuracy of the final product.
- The body replicas are not real human tissue and therefore not subject to any barriers of transportation, import, or use in educational facilities that do not hold an anatomy license. The Monash 3D Anatomy dissection series avoids these and other ethical issues that are raised when dealing with plastinated human remains.