Cholecystitis and cholelithiasis - Erler Zimmer 3D anatomy Series MP2082
erler zimmerMade in ultra-high resolution 3D printing in full color.
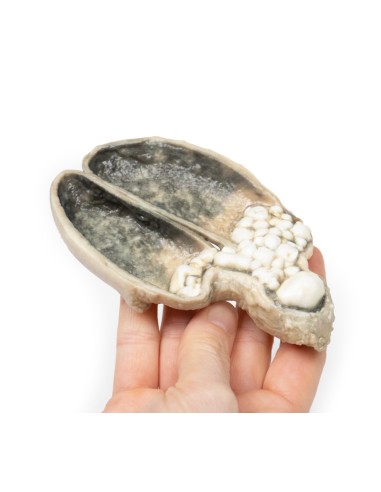
Cholecystitis and Cholelithiasis - Erler Zimmer 3D anatomy Series MP2082
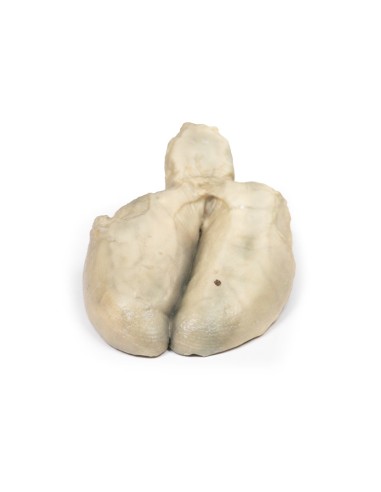
This dissection model highlighting Cholecystitis and Cholelithiasis is part of the exclusive Monash 3D anatomy series, a comprehensive series of human dissections reproduced with ultra-high resolution color 3D printing.
Clinical History.
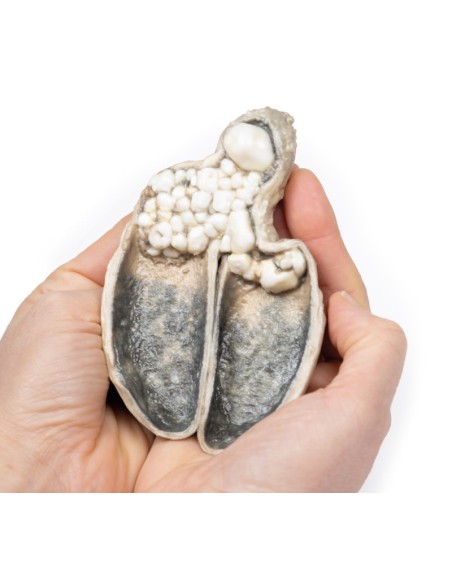
A 60-year-old man heads a history of four episodes of severe abdominal pain in grip during the previous year, each lasting two hours and associated with meals. He presented with a similar attack associated with vomiting and fever. The latter attack did not resolve spontaneously and he underwent cholecystectomy.
Pathology
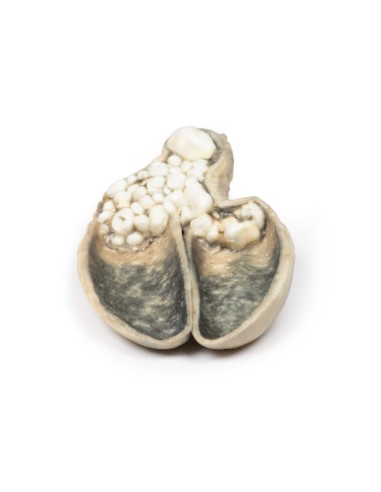
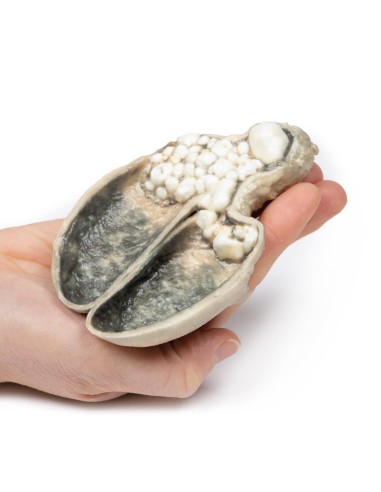
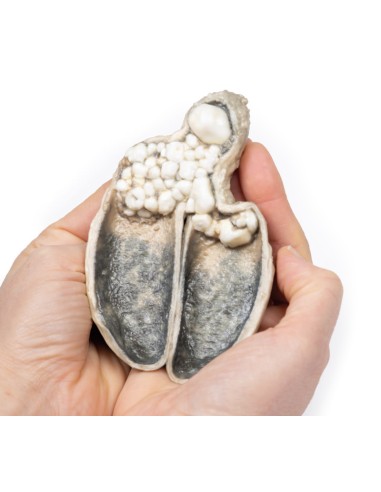
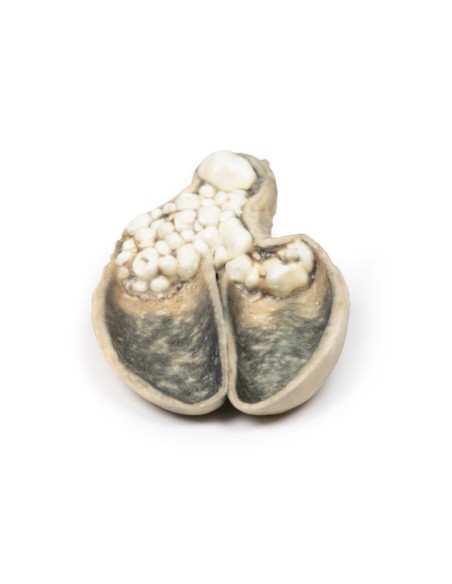
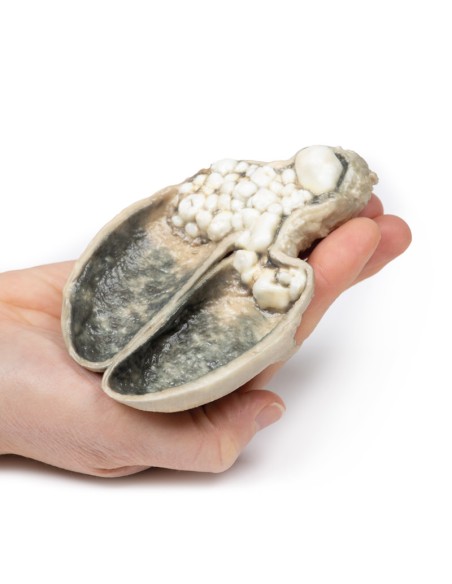
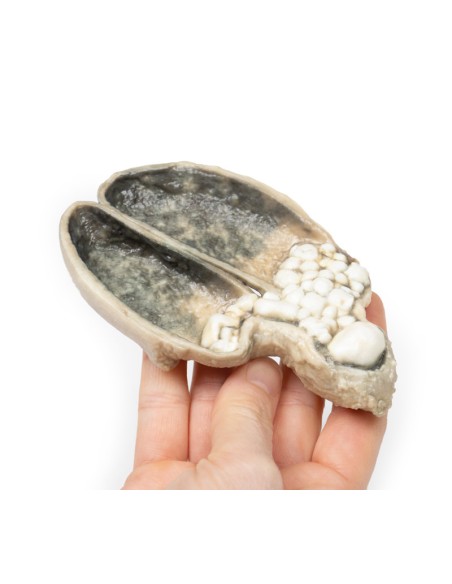
A thick-walled gallbladder was opened to show a thickened hemorrhagic mucosa and many irregular faceted stones. A large stone is affected in the neck of the gallbladder. The serous surface of the gallbladder is congested and has lost its normal luster. This is an example of cholecystitis complicating cholelithiasis (gallstones).
Further information
Acute cholecystitis is characterized by the clinical syndrome of right upper quadrant pain, fever, and jaundice. Gallstones account for the vast majority of acute cholecystitis, with only 5-10% of cases due to other diseases. Chronic cholecystitis may occur, resulting from recurrent attacks and causing fibrosis and thickening of the gallbladder wall. 6-11% of patients with symptomatic gallstones will develop acute cholecystitis. Serum biochemistry will demonstrate leukocytosis with or without obstructive liver function tests. Ultrasonography will show gallstones in the gallbladder, along with wall thickening and an ultrasound Murphy's sign (pain from ultrasound probe pressure). Other imaging modalities include nuclear medicine cholescintographic scans, MRCP (magnetic cholangiopancreatography) and CT scans. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) will provide diagnostic information on biliary obstruction and may also be therapeutic. The causative organisms (if present) will come from the intestinal flora, commonly E coli, Enterococcus, Klebsiella, and Enterobacter. Complications include gangrenous cholecystitis, perforation, cholecystoenteric fistula, or gallstone ileus. The definitive treatment is surgical cholecystectomy.
.
What advantages does the Monash University anatomical dissection collection offer over plastic models or plastinated human specimens?
- Each body replica has been carefully created from selected patient X-ray data or human cadaver specimens selected by a highly trained team of anatomists at the Monash University Center for Human Anatomy Education to illustrate a range of clinically important areas of anatomy with a quality and fidelity that cannot be achieved with conventional anatomical models-this is real anatomy, not stylized anatomy.
- Each body replica has been rigorously checked by a team of highly trained anatomists at the Center for Human Anatomy Education, Monash University, to ensure the anatomical accuracy of the final product.
- The body replicas are not real human tissue and therefore not subject to any barriers of transportation, import, or use in educational facilities that do not hold an anatomy license. The Monash 3D Anatomy dissection series avoids these and other ethical issues that are raised when dealing with plastinated human remains.